nlcpy.random.Generator.gumbel
- Generator.gumbel(self, loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=None)
Draws samples from a Gumbel distribution.
Draws samples from a Gumbel distribution with specified location and scale. For more information on the Gumbel distribution, see Notes below.
- Parameters
- locfloat, optional
The location of the mode of the distribution. Default is 0.
- scalefloat, optional
The scale parameter of the distribution. Default is 1. Must be non-negative.
- sizeint or tuple of ints, optional
Output shape. If the given shape is, e.g.,
(m, n, k), thenm * n * ksamples are drawn.
- Returns
- outndarray
Drawn samples from the parameterized Gumbel distribution.
See also
Generator.weibullDraws samples from a Weibull distribution.
Note
The probability density for the Gumbel distribution is
where
is the mode, a location parameter, and
is the scale parameter.
The function has a mean of
and a variance of
.
Restriction
If loc is neither a scalar nor None : NotImplementedError occurs.
If scale is neither a scalar nor None : NotImplementedError occurs.
Examples
Draw samples from the distribution:
>>> import nlcpy as vp >>> rng = vp.random.default_rng() >>> mu, beta = 0, 0.1 # location and scale >>> s = rng.gumbel(mu, beta, 1000)
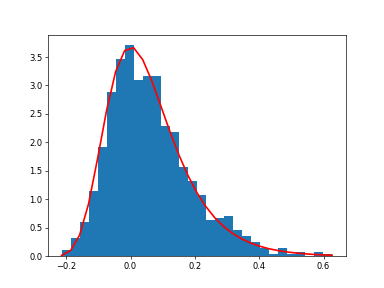
Display the histogram of the samples, along with the probability density function:
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s.get(), 30, density=True) >>> plt.plot(bins, (1/beta)*vp.exp(-(bins - mu)/beta) ... * vp.exp( -vp.exp( -(bins - mu) /beta) ), ... linewidth=2, color='r') ... >>> plt.show()
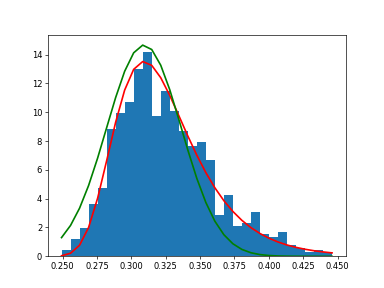
Show how an extreme value distribution can arise from a Gaussian process and compare to a Gaussian:
>>> plt.close() >>> maxima = vp.empty(1000) >>> for i in range(0,1000) : ... a = rng.normal(mu, beta, 1000) ... maxima[i] = a.max() >>> count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(maxima.get(), 30, density=True) >>> beta = vp.std(maxima) * vp.sqrt(6) / vp.pi >>> mu = vp.mean(maxima) - 0.57721*beta >>> plt.plot(bins, (1/beta)*vp.exp(-(bins - mu)/beta) ... * vp.exp(-vp.exp(-(bins - mu)/beta)), ... linewidth=2, color='r') ... >>> plt.plot(bins, 1/(beta * vp.sqrt(2 * vp.pi)) ... * vp.exp(-(bins - mu)**2 / (2 * beta**2)), ... linewidth=2, color='g') ... >>> plt.show()