サンプル: スペクトル解析
目的
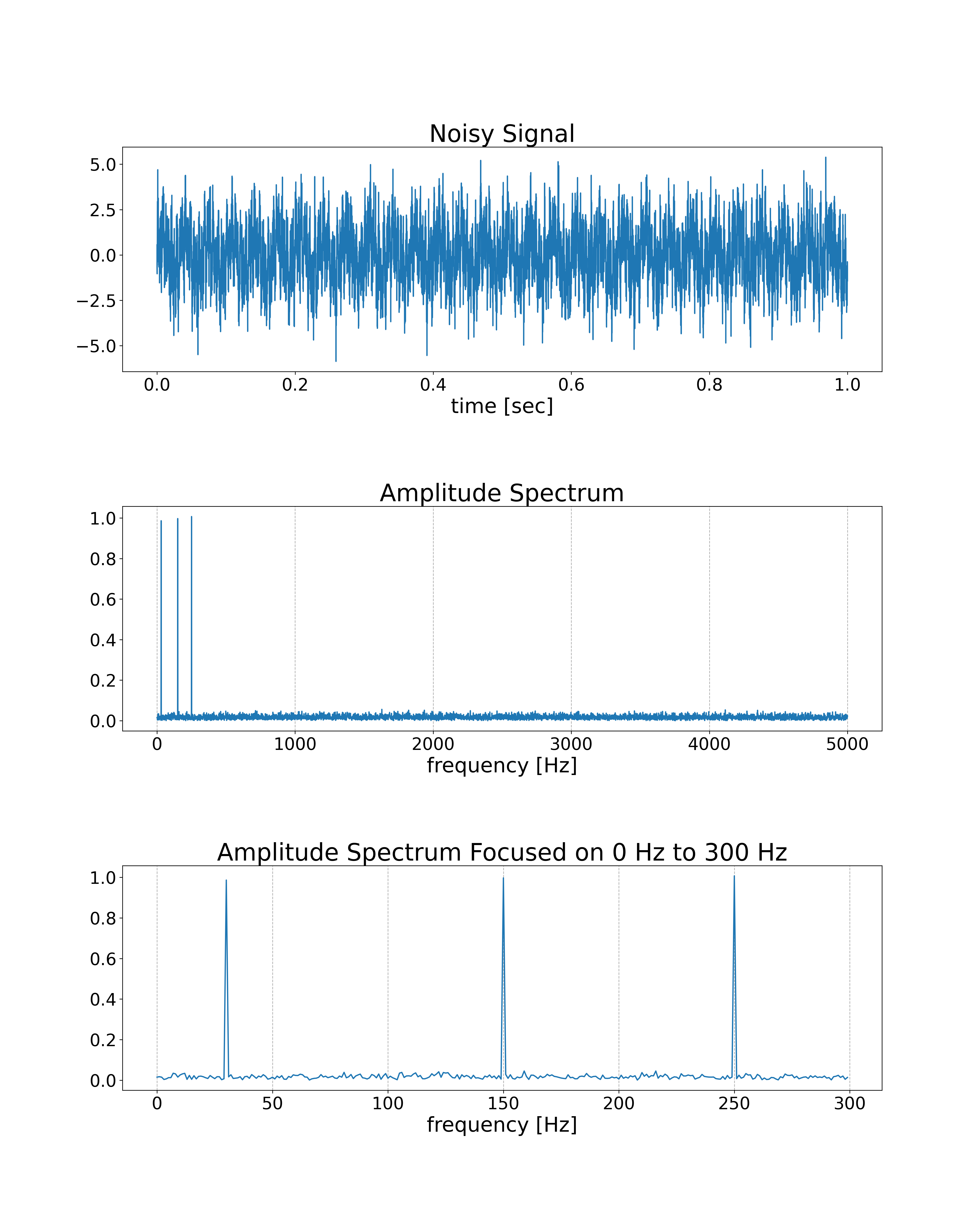
FFTを使用して、ノイズが含まれた信号のスペクトルを解析します。入力信号には、30Hz, 150Hz, および、250Hzの正弦波と正規分布乱数が含まれています。
プログラム
import nlcpy as vp
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
N = 10000 # The number of samples
DT = .0001 # The time step interval
FREQS = [ # The list of frequencies to include in the signal
30,
150,
250
]
def gen_signal():
T = vp.arange(0, N * DT, DT, dtype='f8')
S = vp.zeros(N, dtype='f8')
for f in FREQS:
S += vp.sin(2 * vp.pi * f * T)
# Add noise
S += vp.random.randn(N)
return T, S
def analyze(S):
A = vp.absolute(vp.fft.rfft(S)) / N * 2
F = vp.fft.rfftfreq(N, d=DT)
return A, F
def gen_graph(T, S, A, F):
fig, axes = plt.subplots(3, 1, figsize=(16, 20))
axes[0].set_title('Noisy Signal', fontsize=28)
axes[0].plot(T, S)
axes[0].set_xlabel('time [sec]', fontsize=24)
axes[0].tick_params(labelsize=20)
axes[1].set_title('Amplitude Spectrum', fontsize=28)
axes[1].plot(F[:], A[:])
axes[1].set_xlabel('frequency [Hz]', fontsize=24)
axes[1].grid(axis='x', linestyle='--')
axes[1].tick_params(labelsize=20)
axes[2].set_title('Amplitude Spectrum Focused on 0 Hz to 300 Hz', fontsize=28)
axes[2].plot(F[:300], A[:300])
axes[2].set_xlabel('frequency [Hz]', fontsize=24)
axes[2].grid(axis='x', linestyle='--')
axes[2].tick_params(labelsize=20)
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.6)
plt.savefig('spectrum.png', dpi=300)
if __name__ == '__main__':
T, S = gen_signal()
A, F = analyze(S)
gen_graph(T, S, A, F)
結果